New publication by Henrik Huizinga and Wouter Hooghiemstra in Pharmaceuticals
Our latest publication by Henrik Huizinga and Wouter Hooghiemstra et. al. entitled “Development of Clinical-Grade Durvalumab-680LT and Nivolumab-800CW for Multispectral Fluorescent Imaging of the PD-1/PD-L1 Axis of the Immune Checkpoint Pathway” can be found here.
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are effective against various advanced and metastatic cancers, but patient responses vary and can change over time, complicating treatment prediction. Therefore, better tools for patient stratification, response prediction, and response assessment are needed. This study presents the development and clinical translation of a fluorescently labelled ICI tracer pair used to perform multispectral fluorescent molecular imaging and simultaneously gain spatial and temporal insight in both programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1) expression.
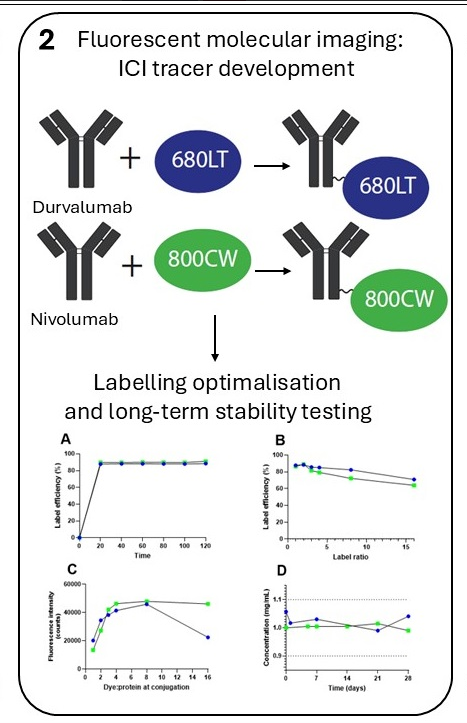
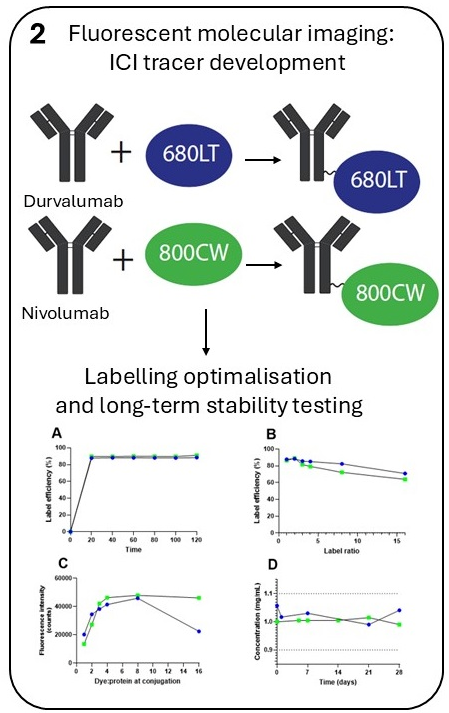
Methods: We conjugated the anti-PD-L1 antibody durvalumab to IRDye 680LT and the anti-PD-1 antibody nivolumab to IRDye 800CW. Tracers were developed and optimized for conjugation efficiency and purity to allow use in clinical trials. Stability was tested up to 12 months. An extended single-dose toxicity study in mice was performed for durvalumab-680LT and the unconjugated IRDye 680LT to demonstrate safety for first-in-human administration.
Results: Durvalumab-680LT and nivolumab-800CW were successfully conjugated and purified. Conjugation optimization resulted in a robust production with labelling efficiencies of ≥88%. Long-term stability study of both tracers showed all parameters within end of shelf-life specifications for at least 12 months at 2–8 °C. No toxic effects were observed in doses up to 1000x the intended human dose for both IRDye 680LT and durvalumab-680LT, which are therefore considered safe for first-in-human use.
Conclusions: We succeeded in the development and clinical translation of two novel fluorescent ICI tracers, durvalumab-680LT and nivolumab-800CW. Moreover, we demonstrated for the first time the safety of IRDye 680LT and durvalumab-680LT, enabling first-in-human use. Together, this makes durvalumab-680LT and nivolumab-800CW suitable for phase I/II clinical trials.
Keywords: fluorescent tracer development; fluorescent molecular imaging; multispectral imaging; immune checkpoint inhibitors; durvalumab; nivolumab; IRDye 680LT; toxicity